Key Takeaways:
- Industrial conveyor belts play a pivotal role in enhancing manufacturing efficiency and productivity.
- Advancements in materials and technology have led to more durable and energy-efficient conveyor systems.
- Integration with automation and smart technologies is transforming the functionality of conveyor belts.
- Sustainable practices in conveyor belt manufacturing are helping to reduce environmental impact.
Introduction
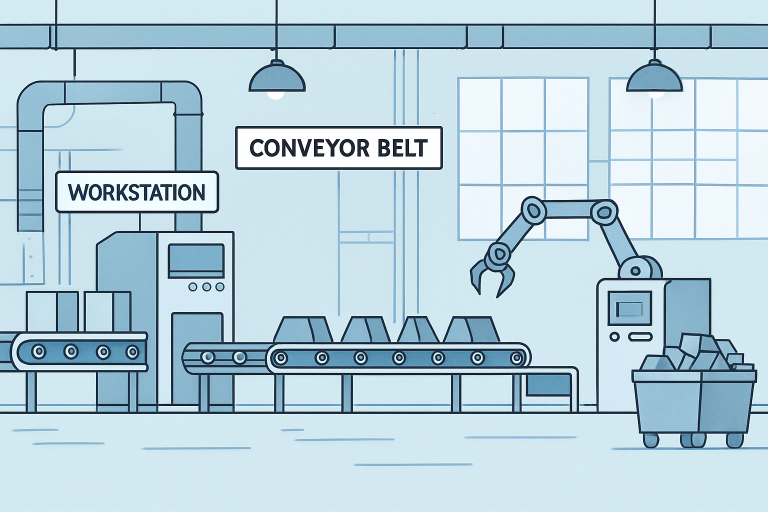
Industrial conveyor belts are fundamental to contemporary manufacturing processes, acting as the backbone of production lines by streamlining the movement of materials and products. These intricate systems have evolved vastly from their rudimentary origins, becoming rallying points for operational efficiency and technological progress. Whether involved in assembly, packaging, or distribution, conveyor belts support the entire manufacturing ecosystem and help reduce downtime and labor needs. It’s not just high-tech factories benefiting even facilities using wire rope Little Rock for their logistical frameworks rely heavily on robust conveyor technologies.
As diverse industries strive to achieve higher output and lower error rates, conveyor belts have emerged as indispensable. Their ability to automate repetitive tasks and maintain consistent workflow means businesses can scale operations without sacrificing product quality or workforce safety. In this way, the humble conveyor belt stands as a symbol of industrial innovation and resilience.
Historical Overview
The story of conveyor belts dates back to the late 1800s, when the first systems were introduced in the mining and agricultural sectors to move bulk goods more efficiently. Early versions were largely limited by the materials and energy sources available, resulting in manual operation and limited adaptability. With the onset of industrialization, motorized belts became mainstream, transforming how factories handled everything from coal and grain to finished consumer products. Eventually, conveyor belts expanded their reach into automotive, electronics, and food processing sectors, growing more versatile with each step forward.
This advancement in conveyor technology mirrored broader trends in manufacturing innovation, notably those driven by the assembly line principles first articulated by Henry Ford. Continuous movement made it easier to scale up production and standardize outputs, which, in turn, fueled the economic expansion that characterized the 20th century.
Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity
Modern manufacturing would be unrecognizable without the contributions of conveyor belts. Their core benefit lies in their ability to automate material handling minimizing manual interventions, reducing errors, and creating a streamlined flow from one production station to the next. Take the automotive industry as an example, where conveyor systems ensure that every component, from engines to exteriors, moves seamlessly down the line for assembly, painting, and quality checks. This not only enhances productivity but also enforces uniformity in production standards.
Beyond the automotive industry, conveyor systems play a crucial role in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, ensuring that materials adhere to strict regulatory and safety guidelines. A recent feature by BBC Future highlights how continuous manufacturing yields faster production cycles and better product tracking, key attributes that ambitious manufacturers simply can’t do without.
Technological Advancements
Innovations in material science have made conveyor belts more robust and adaptable to extreme operating conditions. Fiber-reinforced polymers, high-performance elastomers, and corrosion-resistant alloys contribute to belts that last longer and require less frequent replacement. These materials also resist degradation from chemicals, temperature shifts, and heavy loads common challenges in industrial settings.
The digital revolution has further transformed conveyor systems. By integrating sensors, IoT devices, and advanced monitoring tools, manufacturers can now measure system health in real-time. Predictive maintenance has replaced reactive interventions, minimizing downtime and lowering maintenance costs. According to the Forbes Tech Council, IoT-enabled conveyor belts can automatically detect wear, diagnose bottlenecks, and optimize energy consumption, ensuring maximum uptime and efficiency.
Integration with Automation
The close relationship between conveyor systems and automation is rapidly transforming the nature of manufacturing facilities. Smart conveyor belts, enhanced with AI and machine learning, can dynamically adjust their speed, loading, and routing in response to real-time demands. Predictive analytics enable production managers to anticipate changes in workflow and proactively address inefficiencies.
These smart systems do more than just move materials they collect data, adapt to new tasks, and support continuous improvement initiatives. The result is an ecosystem in which manufacturers can fine-tune their output, reduce energy use, and minimize operational bottlenecks without incurring vast capital investments or undertaking process overhauls.
Sustainability in Conveyor Belt Manufacturing
The push for greener operations is shaping how conveyor belts are designed and manufactured. Today’s belts often incorporate recycled content and renewable materials to help lower emissions and reduce landfill waste. Energy-efficient motors and low-impact designs further help manufacturing facilities meet global sustainability benchmarks, a commitment reflected in industry certifications and client partnerships.
For businesses looking to future-proof their operations, investing in sustainable conveyor systems isn’t just a moral imperative it’s a competitive one. Facilities that prioritize sustainability as a core value benefit from regulatory compliance, cost savings, and an enhanced brand reputation.
Future Trends
The conveyor belt sector continues to undergo dynamic transformation driven by automation and digitization. Artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things are expected to bring about even greater advances in operational transparency and efficiency, such as smarter inventory management and fully autonomous manufacturing lines. Moreover, the ongoing shift toward sustainable materials and closed-loop manufacturing processes indicates that environmental responsibility will shape the next era of conveyor belt innovation.
From supply chain logistics to final packaging, the conveyor belt remains central to the vision of Industry 4.0 and the adoption of smart, sustainable approaches will only accelerate this trend.
Conclusion
Industrial conveyor belts have evolved from basic mechanisms to complex, automated solutions integral to manufacturing worldwide. Their continued advancement highlights their irreplaceable value, whether that’s in boosting efficiency, supporting automation, or fostering sustainability. As new technologies and materials emerge, conveyor belts are set to remain at the forefront of innovation and growth within every industry they touch.