Key Takeaways
- Regular water main testing is crucial for identifying contaminants and mitigating health risks.
- Advanced technologies, including machine learning, are enhancing the efficiency of water main monitoring.
- Community involvement and awareness are vital in maintaining water quality and safety.
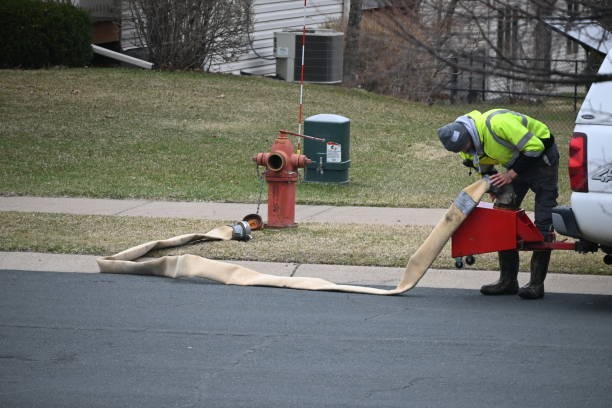
Ensuring the safety and reliability of a community’s water supply is crucial for protecting public health. Regular water main testing forms the backbone of these efforts, helping municipalities detect problems early and safeguard against contamination or infrastructure failure. Specialized equipment, such as a hydrostatic test pump, is often employed to pressure-test water mains and identify weaknesses or leaks before they escalate. Consistent monitoring ensures water quality and provides reassurance to residents about the integrity of their water system. Well-maintained systems rely on testing to detect issues such as bacterial intrusion or chemical seepage early, thereby preventing leaks, property damage, and health hazards. As urban areas grow and infrastructure ages, proactive testing using advanced tech and community engagement is vital. Municipal authorities use real-time data and predictive models for ongoing monitoring, enhancing transparency and accountability. Systematic inspections help address vulnerabilities quickly, especially against new threats such as extreme weather and pollutants, ensuring water security and the modernization of operations.
Importance of Regular Water Main Testing
Testing water mains on a set schedule helps utilities discover leaks, contamination, or pressure loss before these issues disrupt service or pose hazards. Preventive testing is a cornerstone of public health, enabling municipalities to take immediate corrective action when deviations from safety standards are found. It also saves money and resources by reducing the likelihood of costly emergency repairs after a major failure. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, routine testing and monitoring are crucial measures for ensuring the safe delivery of water and meeting regulatory requirements.
Common Contaminants and Their Risks
Water mains can become pathways for hazardous contaminants, such as lead, E. coli, or pesticides, due to infrastructure deterioration or environmental factors. Lead is especially dangerous, and exposure can lead to neurological and developmental deficits in children. Systematic water testing is the first line of defense, identifying sources of contamination—from corroded pipes to cross-connections with polluted groundwater—allowing for targeted intervention. Incidents like the Flint water crisis underscore the severe long-term effects of unchecked contamination.
Technological Advancements in Water Main Monitoring
Emerging technologies are revolutionizing the way cities monitor and maintain their water infrastructure. Tools such as smart sensors, remote data loggers, and AI-driven predictive analytics allow utilities to spot early warning signs of a pipe rupture or contamination event. Machine learning, in particular, can analyze large datasets—combining weather patterns, pipe material age, and historical breakage records—to forecast risk zones and optimize inspection and repair schedules. By shifting toward predictive maintenance, cities reduce downtime and enhance public safety.
Case Studies of Effective Water Main Testing
Several American cities offer success stories that reflect the effectiveness of thorough testing protocols. The City of Phoenix, for instance, analyzes about 1,000 water samples every week, systematically monitoring for pathogens and chemical impurities. This approach not only helps meet federal standards but also builds resident confidence in the quality of tap water. Similarly, cities leveraging technology such as Chicago’s predictive analytics pilot have reported lower rates of main breaks and swifter repair timelines, thanks to continuous risk assessment.
Community Involvement in Water Safety
Fostering robust collaboration between local water authorities and residents improves both oversight and response. Cities like San Francisco partner with community leaders and regional organizations to educate the public on water safety, provide testing kits for at-home sampling, and establish clear channels for reporting any suspicious water quality issues. These measures foster transparency and build trust, enabling quicker, community-driven identification of the potential problems and more effective resolution strategies.
Challenges in Maintaining Water Main Integrity
Water main infrastructure across the United States faces mounting pressures: many systems are decades old, frequently subjected to freeze-thaw cycles, ground movement, and the impacts of nearby construction or wildfires. Such stressors make pipes more prone to fracture or corrosion, increasing the likelihood of service disruptions and contamination events. Financial constraints also limit many municipalities’ abilities to replace or refurbish aging water mains at the pace required. Emergency preparedness plans and infrastructure upgrades remain key to combating these widespread challenges.
Best Practices for Water Main Testing
- Schedule consistent sampling along the entire distribution network to catch contaminants early.
- Adopt real-time monitoring technologies for continual risk assessment.
- Engage residents by providing them with information, clear reporting mechanisms, and opportunities for participation.
- Maintain open access to results and action plans to ensure ongoing transparency and accountability.
When consistently applied, these practices reduce the likelihood of unexpected water crises and help ensure the continuous delivery of safe and reliable water to local communities.
Conclusion
Regular, comprehensive water main testing plays a crucial role in safeguarding public health and maintaining community resilience against water system failures. By combining state-of-the-art technologies, well-established best practices, and active community involvement, cities are better equipped to address both present and future challenges in water system management. Strategic investment in infrastructure and regular assessment enable municipalities to deliver on the promise of safe, clean water for all residents—now and for generations to come.