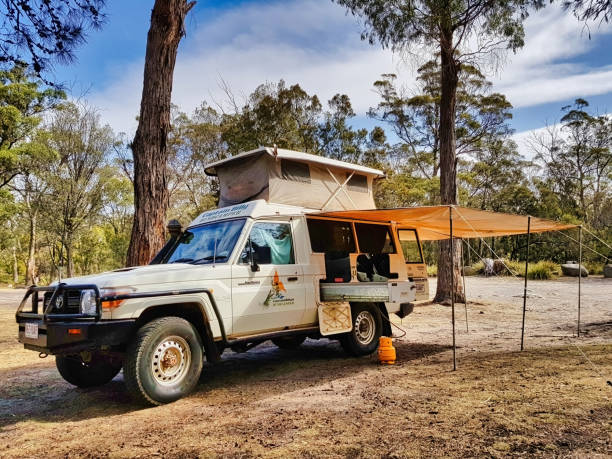
Selecting the right outdoor shelter system can make or break your off-road experience, and finding a top-quality 4wd awning requires careful consideration of multiple technical factors. Modern awning technology has evolved significantly, incorporating advanced materials and engineering principles that directly impact durability, weather resistance, and ease of deployment. This comprehensive analysis examines the critical specifications and performance characteristics that distinguish premium awning systems from basic alternatives, providing the technical insights needed to make an informed purchasing decision for serious outdoor enthusiasts.
Material Construction and Fabric Technology
The fabric composition determines an awning’s lifespan and weather resistance capabilities. Premium awnings typically utilize ripstop polyester or canvas materials with PU (polyurethane) coatings that provide superior waterproofing compared to standard PVC alternatives. Ripstop construction features reinforcement threads woven at regular intervals, creating a grid pattern that prevents tear propagation – a crucial factor when dealing with high winds or accidental snags.
Canvas awnings, while heavier, offer exceptional durability and UV resistance. The weave density, measured in grams per square meter, directly correlates with longevity. Quality canvas awnings typically range from 280-320 GSM, providing optimal balance between weight and durability. The waterproof rating, expressed in millimeters, should exceed 3000mm for reliable weather protection.
Frame Construction and Mounting Systems
Aluminum frame construction dominates the premium market due to its strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. Anodized aluminum provides additional protection against oxidation, particularly important in coastal environments. Frame diameter and wall thickness significantly impact structural integrity – quality awnings feature 25mm diameter arms with minimum 1.5mm wall thickness.
Mounting bracket design varies considerably between manufacturers. Vehicle-specific brackets provide superior stability compared to universal systems, distributing load forces more effectively across mounting points. Consider brackets with adjustable positioning to accommodate different vehicle configurations and roof rack systems.
Deployment Mechanisms and Ease of Use
Spring-loaded deployment systems have largely replaced manual crank mechanisms in quality awnings. These systems utilize torsion springs within the roller tube to assist with extension and retraction, reducing setup time and physical effort. However, spring tension must be properly calibrated – insufficient tension causes sagging, while excessive tension creates deployment difficulties.
Gas strut-assisted systems represent the premium option, providing consistent deployment force regardless of weather conditions or fabric moisture content. Quality gas struts maintain pressure across temperature ranges from -20°C to +60°C, ensuring reliable operation in diverse climates.
Wind Rating and Structural Stability
Wind resistance specifications vary dramatically between manufacturers, with quality awnings rated for sustained winds of 25-35 km/h when properly guyed out. However, these ratings assume optimal setup conditions with all guy ropes and pegs deployed correctly. The aerodynamic profile of the awning significantly impacts wind performance – models with adjustable pitch angles provide better wind shedding capabilities.
Support arm design influences stability substantially. Telescoping arms with internal cable tensioning systems provide superior rigidity compared to simple pin-adjustment mechanisms. Premium awnings incorporate wind-sensing technology that automatically adjusts tension to prevent damage during unexpected gusts.
Size Considerations and Coverage Area
Awning size selection depends on intended use patterns and vehicle dimensions. Standard sizes range from 2.5m to 4m in length, with projection distances from 2m to 2.5m. However, effective coverage area depends on mounting height and ground slope conditions. A 2.5m x 2.5m awning mounted at 2.8m height provides approximately 6.25 square meters of ground coverage under ideal conditions.
Consider the relationship between awning size and vehicle stability – larger awnings create increased wind loading that can affect vehicle handling in exposed conditions. Weight distribution also becomes critical with larger installations, potentially requiring load distribution plates to prevent roof damage.